Health
| Parvoviral enteritis (typhus)
Carre disease (canine distemper)
|
Erlichiwsi | Leukocytes |
3. Alternatively injection (Antimonioychos Antimoniate) once daily for 28 days.
- a. acute phase: usually occurs during the spring months, shortly after the appearance of ticks. The animal that suffers, usually has his skin ticks. The first clinical symptoms typically occur 10-20 days after infection and is light format: Wiggly fever, partial or complete loss of appetite, depression, little weight loss.
Rarely observed slight swelling of the lymph nodes, slight clouding of the cornea *, conjunctivitis *, Interstitial pneumonia, swelling of extremities and the scrotum and vomiting. In some cases likely to observe small hemorrhages.
At this stage, despite the fact that the blood test is usually observed intense thrombocytopenia (drop in the number of blood platelets, which naturally must lie between 200,000 and 450,000), there are no typically formal haemorrhagic manifestations of disease that characterize the hemorrhagic syndrome mood (petechiae on the skin and mucous membranes, epistaxis, hematuria, etc.)
This first "febrile stage lasts from 4 days to 3 weeks, followed by the ' subclinical phase?. - (b). Subclinical phase: during this phase, which lasts 40-120 days, although the clinical symptoms subside and the animal appears to have cured, haematological findings are usually similar to those of acute phase, i.e. Leukocytosis, hypoplastic anemia and intense thrombocytopenia.
- (c). Chronic phase: the chronic phase is the final phase of the disease. The usual symptoms are: prostration and lithargikotita, fever, pallor mucous, progressive weight loss, petechiae and ecchymoses in skin and mucous membranes, and nosebleed unilateral or bilateral.
The nosebleed typically occurs abruptly and is particularly intense and persistent. Result of hemorrhaging is severe acute haemorrhagic anaemia.
Usually the chronic phase of the disease appears during the autumn or winter months, and so the more times the sufferer animals don't have ticks on their skin during this phase.
In some breeds of dogs such as in dogs, it is possible the chronic phase shows two different forms, which are characterized as "mild" and as "severe chronic" form.
The "mild" form in dogs is not very different from the chronic form observed in other breeds.
In contrast, the "severe chronic" form, is serious and often fatal, even if applied treatment. In this format, presents acute clinical signs 60-120 days after infection, and include acute panleukopenia, moodiness, loss of appetite, weight loss and acute hemorrhages from the nasal cavities, gums, the urinary tract, the digestive etc. Secondary bacterial infections often coexist.
In dogs that do not apply treatment, death occurs within a few hours to a few days after the onset of hemorrhages.
Diagnosis-Treatment: of course, the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, not an object's owner, but the vet.
The veterinarian has the necessary knowledge needed to properly address the problem on the one hand, but also to properly diagnose. Because the diagnosis is not so simple from the non-specific, since the clinical symptoms are not indicative of Erlichiwsis. Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and anemia occur in other diseases, such as Babesiosis. The hemorrhages, especially bleeding from the nasal cavities, it can be due to Leishmaniasis (Kala-azar), poisoning, Tumours-tumours of the nasal cavities, or foreign bodies (e.g. thorns). Liability of the owner is the quick visit to the vet as soon as they realized that the animal show anything abnormal.
We should emphasise that the canine Ehrlichiosis, if diagnosed in time and given the proper treatment, is a disease that is cured in most cases.
Prevention: prevention of Erlichiwsis consists in the systematic and careful fight ticks, so onto the body of animals, and the environment. The implementation of preventive instruments (antiparasitic collars and formulations), before the appearance of ticks on an animal, is the best response to the risk of contamination.
Relationship with the public health: the canine Ehrlichiosis does not offend the man. Therefore contact with diseased animals and treatment to them, does not create risks for owners.
Thrombocytes or Platelets: Going for blood cells produced in the bone marrow and play a key role in blood clotting. In a healthy dog, the number of thrombokyttarwn ranges from 200,000-450,000 per cubic chiliosto blood. The fall of thrombokyttarwn in low levels, involves the inability of the Agency to stop the bleeding
Leukocytes. : this is the white blood cells of the blood. Produced in bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, etc. Is the defensive units of the Organization in the fight against infections, both "eating" germs and by producing antibodies. In a healthy dog, the number of leukocytes in the range from 6000-18000 per cubic millimeter of blood. The fall in the number of leukocytes in low levels entails the reduction of the organism to resist diafors infections.
Pankytopenia: It lessening of all blood cells. A reduction in the number of both red blood cells and white blood cells and thrombokyttarwn.
Cornea: the transparent anterior portion of the eye.
Conjunctivitis: Inflammation of the conjunctiva, the Interior Department of the eyelids that IE comes into contact with the eyes, which is characterized by intense redness and pywdwn ekkrimmatwn presence.
Anemia: the fall of the number mean time red blood cells, or hemoglobin aiposotitas contained in blood cells, and is characterized by pallor (whitewashing) mucous membranes. Especially when there are internal bleeding, mucous membranes exhibit color porcelain
Nikos Triantafillou-Veterinarian
Etiology
The demodikwsi is caused by the parasite Demodex Canis which is found in the skin of healthy dogs (hair follicles and sebaceous glands). Dogs are infected by their mothers in the early days (3-4) in their lives, with direct contact.
Pathogenesis
According to studies, the Demodex canis can be found on the skin of each dog but to manifest the disease should there be predisposing factors such as poor hygiene, diet, often bathrooms, other co-existing illnesses (diabetes, cancer, etc.). An important role plays the hereditary predisposition. The demodikwsi is not transmitted to other dogs or humans.
Symptomatology
The lesions are found in the skin and include Erythema, allwpekia, yperchrwmia, scabs, swelling (swelling), skin pustules, ulcers, leichinopoiisi, fistulas.
Distinguished 3 forms of demodicosis:
- Localized form-with mainly young dogs (3-6 months). Appears with these lesions on the Forelegs and on the head. There is mild or no itching. Rarely evolve into generalized
- Generalized-diseased young and adult dogs. Some dog breeds are predisposed to this format, like the Boxer, Chow chow, Doberman, Molossians, etc.
Are there any known lesions of demodicosis but in heavier form-allwpekia, swelling, blistering, fistulas, etc. and intense itching usually due to purulent dermatitis. Yet it is possible to see fever, Lymphadenopathy, otitis externa, weakness, anorexia, septicemia with lethal outcome.
- Demodiktiki Pododermatitida. The lesions are mostly found in the lower parts of the legs. Sometimes these are lesions that persist after treatment of generalized format.
Diagnosis
Made from the veterinarian after microscopic examination of scrapings from the skin lesions. Rarely will need skin biopsy.
Forecast
Is good in localized form and in young animals. In generalized form mainly of adult dogs, the prognosis is guarded because many times the demodikwsi accompanied by other serious diseases that affect the health of the animal.
Treatment
In localized form often enhancing self-healing without any treatment.
In the generalized form of treatment is difficult and requires good cooperation between owner and veterinarian. The duration of treatment is great (often for 3-6 months). Includes pesticides medications (amitraz, ivermectin, mimplemykini) for external and systemic. Often preceded by treatment with antibiotics and antiseptic baths for purulent dermatitis.
Prevention
Recommended sterilization on female dogs that gave birth to sick puppies as well as exclusion from the breeding of animals in their industry was shaken by demodikwsi life.
Recently released an ampoule with ultra score. Used 1 per 15 days for 3 consecutive times and meta as simple ampoules for ticks and psiloys
The hip dysplasia of hip dysplasia in dogs is a condition that involves either one or both hip joints, in relation with the supportive and active role. The joint that connects the rear end with the trunk of the animal. The articular surfaces are that of the femur and the acetabulum. The acetabulum is none other than a circular Dent, that surrounds the femur head, to allow movement, but while the holds. These surfaces, like all articular surfaces overlap by a protective soft tissue, the articular cartilage. The hinge in order to be fully functional needs to be properly developed. In some cases, however, this is not the case. The hinge has an abnormal shape, something that leads to the weakening of. This phenomenon is called hip dysplasia. Caused by a laxit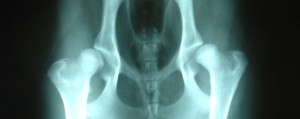 y of muscles, connective tissue, but also links that support articulation. The looseness allows non-intimate contact of the bones, resulting in a change in the size and shape of articular surfaces. Most dysplastika dogs are born with normal joints, because of their genetic profile, but also other factors acquire the above loose coupling of components of articulation, with the result that eventually compromised.
y of muscles, connective tissue, but also links that support articulation. The looseness allows non-intimate contact of the bones, resulting in a change in the size and shape of articular surfaces. Most dysplastika dogs are born with normal joints, because of their genetic profile, but also other factors acquire the above loose coupling of components of articulation, with the result that eventually compromised.
The symptoms are primarily due to the development of inflammation in the joint due to abnormal friction of articular surfaces between them. Dogs of all ages can experience. In severe cases, puppies just 5 months they begin to show pain and discomfort during exercise. Without intervention the infected animals are in older age may not be able to even walk. In most cases, however, symptoms occur in older animals. Specific symptoms resemble very an arthritis in the hip. That is the dog walking way alters or is hesitant to go. Still reacts in trying to curb or to extend such articulation. Also finds it difficult to climb stairs and is less drastiros. Eventually the hindlimb muscles atrofoyn and the dog is unable to stand alone. Often the owner of such animal ignores all these symptoms considering that due to the advanced age of the pet, while startled when they subside with proper treatment. Hip Dysplasia is a condition that occurs with greater frequency in large breeds of dogs, like German Shepherd, great Dane, Labrador Retriever, GoldenRetriever Rottweiller, and Saint Bernard. But that does not preclude his appearance and other tribes. Concerns mainly purebred animals.
The exact etiology of hip dysplasia is not known and so it only matters can be made. The factors that may be responsible is:
1.-Genetic: it is generally accepted that genes play an important role in the onset of disease. For this reason, animals that are diegnwsmena with hip dysplasia is not used for reproductive purposes, as it is very likely their descendants to suffer from the same problem. Instead, two animals in the family history is absent the disease can cross with relative safety.
2.-Diet: it seems that overeating and obesity have great influence on the intensity of symptoms, the obese animal overload when very an already dysfunctional joint.
3.-Drill: too much exercise can aggravate the articulation and intensify symptoms. Nevertheless, each animal should be practiced daily, just avoiding the excesses.
The diagnosis is made with a combination of symptoms, findings of physical examination by the veterinarian and radiological examination. The definitive diagnosis is not always feasible. The above means, nevertheless constitute a very good guide for the assessment of the condition of the animal.
Antipetwpisi
Hip Dysplasia can be treated both surgically and conservatively, with granting i.e. medicinal substances. The choice of method has to do with the age, size and condition of the animal. The surgical methods are varied and the choice of the most suitable for the situation of the joint and the age of the animal. Many times, however, in order to avoid the burden of the dog with surgeries, selected the conservative treatment. This includes administering medications that slow joint deterioration and reduce pain. Additional desired animal's weight control and physiotherapeutic treatment. In any case, full cure is not possible as many times the damage is not reversible. It should be stressed the positive effect of nutritional supplements on specific disease.
Effective prevention is not possible. The only way to avoid the occurrence of disease, is with the right choice of animals for breeding, but that does not mean that an animal, even if it comes from healthy parents, they won't ever become ill. Finally a proper diet, daily not excessive exercise and regular veterinary inspection measures for the better health of the animal.
Canine leishmaniasis (HCG) is a severe and fatal zoonosis due mainly to the Protozoan Leismania infatum.
Distinguished 3 Leismaniasis formats:
1. The skin (most common)
2. Visceral – Well Azar
3. The blennogoniki – rarer usually Leismania Braziliensis
 y they usually sleep. Fly at a distance of 2 km.
y they usually sleep. Fly at a distance of 2 km. Once diagnosed the Leismaniasis with diagnostic kit Elisa tests must be done to control the vital organs (liver, kidneys, etc) for any attack.
The Leismaniasi is a deadly disease that is rampant among others and our country.
Proper prevention, early diagnosis, effective treatment and monitoring of cargo of sick animal background has produced spectacular results in recovery as it helps in controlling the disease and limit the outbreaks.
The diagnosis can be made with a special blood test at the vet clinic within 10 minutes or in collaboration with a laboratory from the first 2 weeks after infection.
For the treatment of disease using a combination of drugs aimed at killing the adult parasites (Melarsominis Injections with a distance of 1 month between them) combined with rigorous containment of animal and administration of aspirin for thromboembolism prevention and gradual elimination of mikrofilariwn with specific antiparasitic pills (Milbemax, Interceptor) in monthly-diminiaia basis for over two years. The use of preventive injections for 6-month prevention not recommended due to possible intoxication of the animal based on studies that have been done.
It is therefore extremely important to not forget the annual or biannual check up of our dog and should demand be checked and for dirofilaria.
